Skin cancer is the uncontrollable growth of abnormal skin cells from any of the layers that make up the skin. It one of the most common cancers in the world and it affects people of all skin types.
It mostly affects areas of the skin exposed to the sun like neck, face, ears, lips, arms & on the legs of women. But it can also occur on other areas of the body like genital area, palms of the hand & beneath your nails
Most cases of skin cancer are caused by skin damage that happens from so much exposure to the sun. This damage can happen over a long period of time.
Most people with a history of overexposure to the sun during childhood years have a greater risk of developing both Basal cell carcinoma and Squamous cell carcinoma. Also, since people are living longer, it is assumed they will be exposed to more sunlight over their lifetime.
The skin is made up of 2 main layers: the epidermis on the outside and the dermis under. Skin cancer usually begins in your skin’s top layer known as epidermis. The epidermis is made up of the following cells:
- Squamous cells is the thickest layer of the epidermis which lies just below the outer surface and act as the skin’s inner lining.
- Basal cells, which produce new skin cells, sit beneath the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes — which produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its normal colour. They are located in the lower part of your epidermis.
Types of skin cancer
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) usually affects the areas of the body that is most exposed to sunlight or UV radiation such as your neck or face.
It is sometimes called a rodent ulcer or may look like a sore that won’t heal. Most BCC does not usually spread to other parts of the body and most people are always cured after treatment. However some can be fast growing and may spread into the bones.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) starts from the squamous cells, that make up the middle and outer layers of the skin. It also affects the sun-exposed parts of the body. Meanwhile, people with darker skin are more likely to develop SCC on areas that aren’t often exposed to the sun.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) may appear as appears as a firm red nodule, flat sore with a scaly crust, a red sore or rough patch inside your mouth or red, raised patch or warlike sore on or in the anus or on your genitals
Melanoma
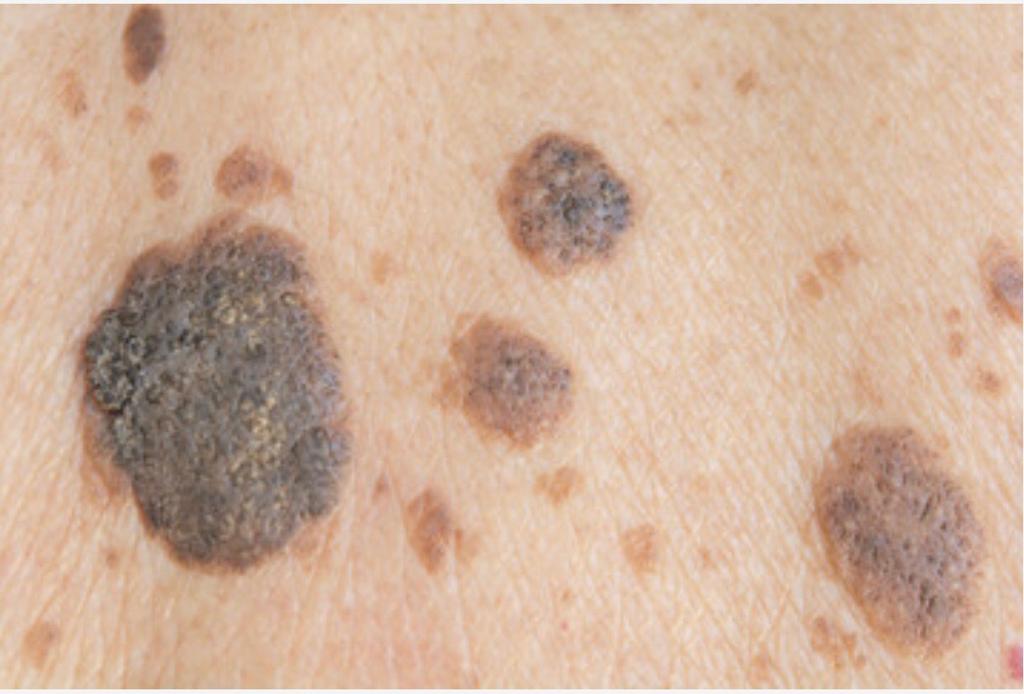
Melanoma (also called malignant melanoma) is a cancer that usually starts from the melanocytes. They are usually more aggressive than the other two types of skin cancer. It can start in a normal looking skin or from an existing mole which then becomes cancerous.
It is important to identify and treat melanoma as early as possible because it can spread deeper into layers of the skin. Also, if Melanoma cells (melanocytes) get into the lymphatic system or the blood, they can move easily into other parts of the body. There are four different types of melanoma. They are Superficial spreading melanoma, Nodular melanoma. Lentigo maligna melanoma and Acral lentiginous melanoma.
The appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole is the most common sign of melanoma. Other signs include:
- A large brownish spot with darker speckles
- Dark lesions on your palms, soles, fingertips or toes, or on mucous membranes lining your mouth, nose, vagina or anus
- A small lesion with an irregular border and portions that appear red, pink, white, blue or blue-black
- A painful lesion that itches or burns