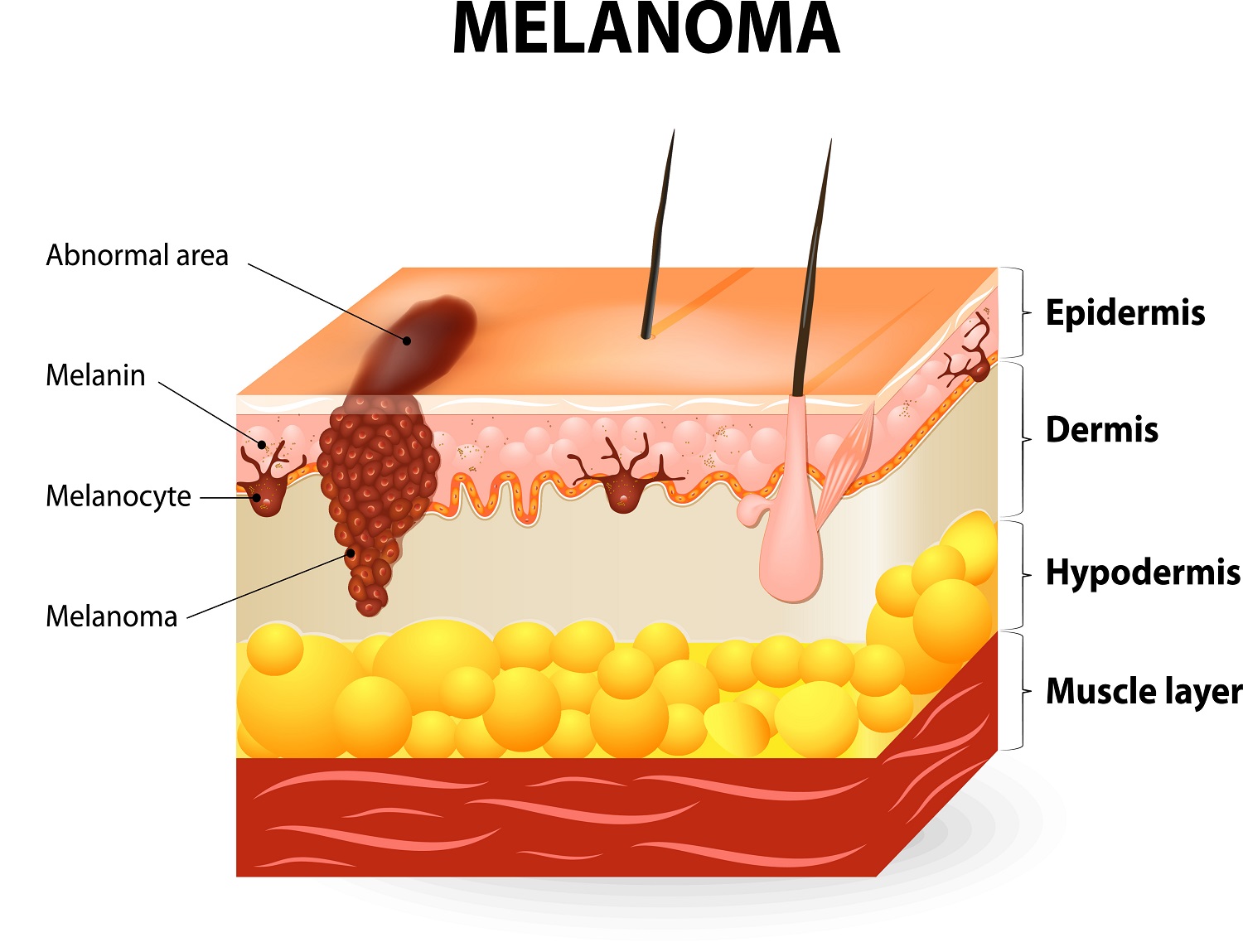
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. It affects melanocytes. These are the skin cells responsible for pigmentation. This type of skin cancer is one of the dangerous ones because of its aggressive nature. Melanoma can quickly spread to other organs if failed to diagnose in the early stages.
Melanoma can occur in different variations. These can be in any size, shape, or color. It is the reason that it is difficult to comprehend the warning signs of the disease. People who are aware of the presentation of the disease can catch the disease earlier. With the help of this, doctors can improve the outlook of the disease.
Prevalence in Africa
Melanoma was once a rare type of cancer. However, the incidence of this type of cancer is gradually increasing all over the world. It affects light–skinned people more than dark–skinned people. This is the reason that Melanoma is very rare in African countries. The most common type of melanoma in Africa is the acral lentiginous subtype.
According to a study in Nigeria 15 cases of melanoma were present in the region within 11 years. These patients presented melanoma in the feet and limbs. The majority of these melanomas were diagnosed at stage III. It makes the process of recovery crucial. However, because African have higher levels of melanin. There remain protected from the cancerous effects of melanoma.
Types of Melanoma
The types of melanoma depend on the area of growth and nature. The four types of melanoma include the following
-
Superficial spreading melanoma
This type of melanoma is the most common. It can invade an already existing mole or can lead to the formation of a new lesion. In the initial phase, it tends to grow on the surface of the skin. In later phases, it penetrates deep within the skin. Upper back, torso portion in men and legs in women are the most common sites of infection. The melanoma can appear to be flat or slightly raised with uneven borders. It does not have any pigmentation and hence can be of the same color as the skin tone.
-
Lentigo Maligna
This type of melanoma most commonly affects people in their old age. It usually affects the skin that is mostly exposed to the sun. These include the face, arms, ears, and the upper torso region. The color of this type of melanoma is bluish–black. However, it can also be in a shade of brown. If this type of cancer spreads farther from the site of origin, it is called lentigo malignant melanoma.
-
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
This type most commonly affects individuals with dark skin color. It is the reason it is most common in Africa. It is present in places that are hard to notice. These include the nails, palms, or even soles. It is black to brown.
-
Nodular Melanoma
This type is the most aggressive form of the disease. It is present in ten to fifteen percent of all cases. The reason that it is dangerous is that it grows faster than the other types. Moreover, it penetrates deeper, as well. It most commonly affects the torso, legs, arms, and scalp. Nodular melanoma appears in the form of a bump on the skin. The melanoma can be blue to black. There may also be a variation in color, which may include from red to pink.
Symptoms of Melanoma
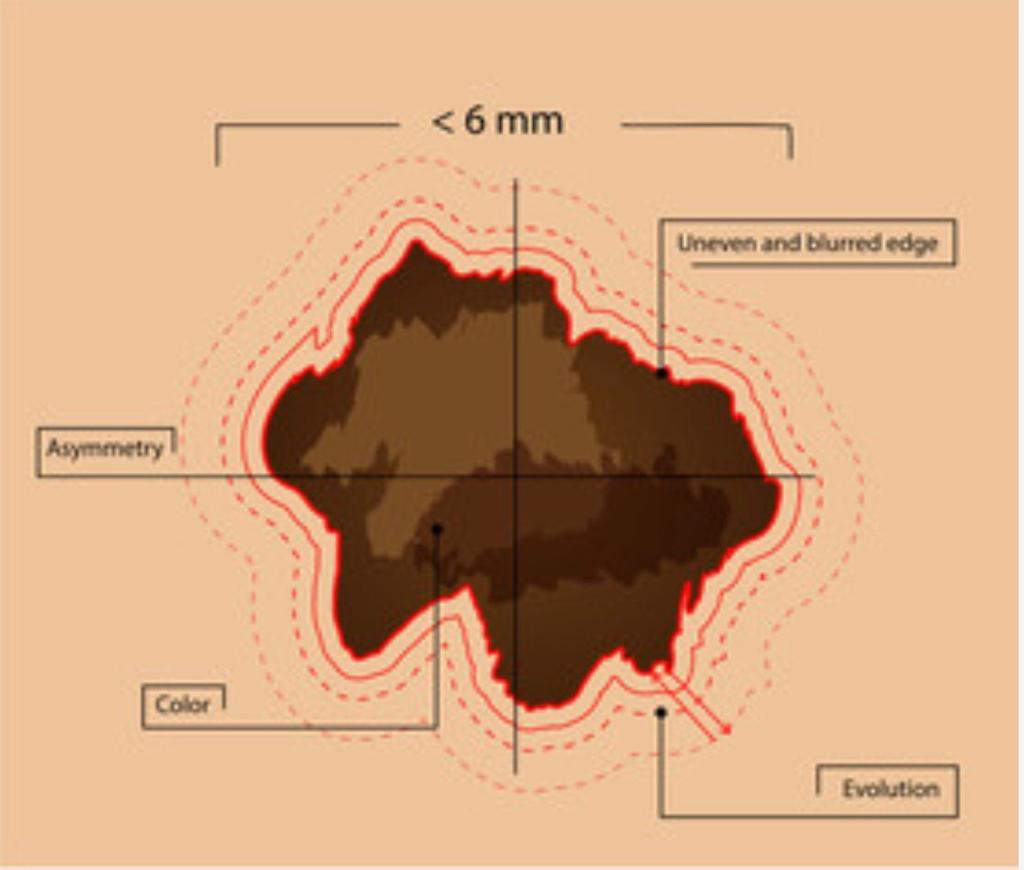
- The clinical symptoms of melanoma usually involve a lump. Certain characteristics indicate a clear melanoma. The doctors refer to it as the ABCDE rules. ABCDE rules help in the physical characterization of the lump A: Asymmetrical shape
B: Irregularity in border
C: Variations in color
D: Diameter of more than six millimeter
E: Elevated surface.
STAGING
Staging of the melanoma helps in the treatment. That is because the staging helps to find out the depth and spread of the melanoma. AJCC has formed the following stages of the cancer
- T Stage of the disease helps to find out the ulceration and thickness of the tumor.
- N (Nodal) stage of the disease helps to find out the involvement of the tumor in the lymph nodes.
- M (Metastatic) stage of the disease helps to find out whether the tumor has metastasized. In other words, it means that the tumor has spread to other parts of the body. It includes skin, lymph nodes, lungs, or viscera.
- Stage 0 (In situ)
The tumors remain only in the upper layer of the skin. There is no penetration to other layers of the skin. Furthermore, the disease has not metastasized to other parts of the body.
-
Stage I
At this stage, melanoma is 2 millimeters thick. Evidence of ulceration may or may not be present. There are two subtypes of this stage.
-
Stage II
At this stage, melanoma has ulceration. Stage II melanoma does not spread to the lymph nodes. There are three subtypes of stage II melanoma.
-
Stage II
At this stage, the melanoma has spread in nearby sites. There are three subtypes of stage III melanoma.
-
Stage IV
At this stage, the melanoma has spread far beyond the regional sites. This stage of melanoma is the most advanced form of this cancer. It means that it has spread to other parts of the body. It includes the lungs, brain, and bones. Brain metastases are a specific type of stage IV melanoma. It is the most complicated form of the disease.
Treatment of Melanoma
- Surgical Excision
Treatment of primary types of melanomas involves surgical excision. It is a better outcome of the disease because of the high survival rate.
-
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy is ineffective for melanoma. Hence, clinicians use chemotherapeutics with a combination of Dacarbazine. FDA approves the use of following medicines for the treatment of melanoma
- Dacarbazine
- Dimethyltriazenolimidazol Carboxamide (DTIC)
REFERENCES
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3074354/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4346328/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4346328/